Security is no longer optional — it’s a fundamental part of modern software development. The OWASP Top 10 is a globally recognized list of the most critical security risks to web applications, published by the Open Worldwide Application Security Project (OWASP).
This list serves as an industry-standard reference point for developers, testers, security professionals, and decision-makers to understand where application threats are most likely to occur.
What Is the OWASP Top 10?
The OWASP Top 10 is a regularly updated report outlining the most pressing security vulnerabilities in web applications. It reflects real-world threat intelligence gathered from bug bounty programs, academic research, and penetration testing results.
Organizations use the OWASP Top 10 as a baseline for:
– Security awareness and training
- Code reviews and secure coding standards
- Risk assessment and remediation planning
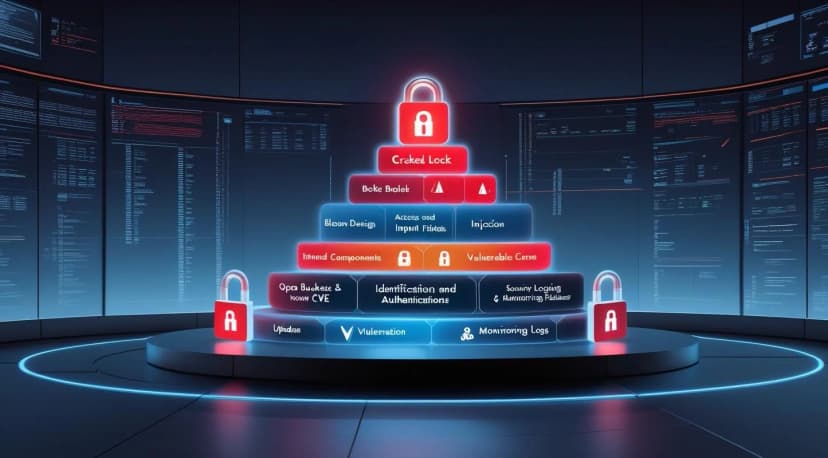
OWASP Top 10 Security Vulnerabilities (Latest Edition)
- Broken Access Control
Unauthorized users can access restricted functions or data.
Mitigation: Enforce role-based access and deny by default. - Cryptographic Failures
Weak or improperly implemented cryptography leads to data exposure.
Mitigation: Use strong encryption and secure key management. - Injection
Attacker injects malicious code via input fields.
Mitigation: Use parameterized queries and validate all input. - Insecure Design
Poor architecture or design choices lead to system-level flaws.
Mitigation: Apply secure design patterns early in development. - Security Misconfiguration
Default settings or exposed services increase risk.
Mitigation: Harden configurations and conduct regular reviews. - Vulnerable and Outdated Components
Unpatched libraries or frameworks introduce known exploits.
Mitigation: Use SCA tools and update dependencies regularly. - Identification and Authentication Failures
Weak login handling or poor session tracking.
Mitigation: Enforce MFA, secure password policies, and session timeouts. - Software and Data Integrity Failures
CI/CD pipeline or update mechanisms are exploited.
Mitigation: Use checksums, signed packages, and secure deployment. - Security Logging and Monitoring Failures
Delayed response to attacks due to lack of visibility.
Mitigation: Implement centralized logging and alerts. - Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF)
App makes requests to unintended internal resources.
Mitigation: Whitelist destinations and validate URLs.
Practical Use of OWASP Top 10 in QA & Dev Teams
- Integrate into SDLC: Use OWASP categories in threat modeling and testing.
- Automated Scanning: Tools like OWASP ZAP and Burp Suite catch common flaws early.
- Training & Awareness: Train QA and developers regularly on secure coding practices.
Tools That Help Detect OWASP Vulnerabilities
| Tool | Use Case |
|---|---|
| OWASP ZAP | DAST scanning and security testing |
| SonarQube | Static code analysis |
| Burp Suite | Manual and automated penetration testing |
| Fortify SCA | Static security scanning of source code |
| Nessus/Qualys | Infrastructure and network-level vulnerability scans |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How often is the OWASP Top 10 updated?
A: Every 2–3 years, based on real-world data and expert input.
Q: Are mobile applications also covered by OWASP?
A: Yes, OWASP maintains dedicated lists for mobile and API security.
Q: Can OWASP vulnerabilities be completely eliminated?
A: Not entirely, but awareness and proactive practices significantly reduce risks.
Conclusion
The OWASP Top 10 serves as a foundation for secure web development. Addressing these vulnerabilities reduces your attack surface, improves compliance, and boosts application trustworthiness.
At Testriq QA Lab LLP, we help implement OWASP-aligned security testing strategies that protect your applications from modern threats.
👉 Talk to a Security Testing Expert
About Nandini Yadav
Expert in Software Testing Tools with years of experience in software testing and quality assurance.
Found this article helpful?
Share it with your team!